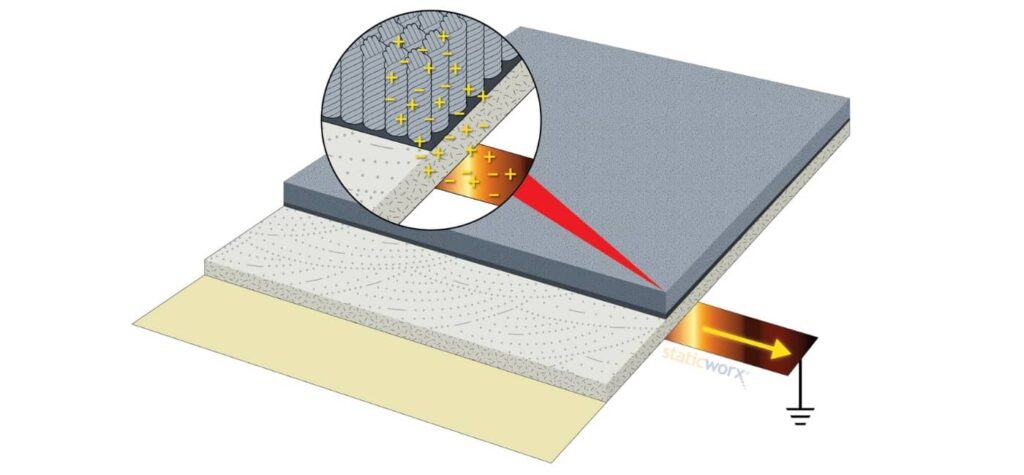
How to Ground an ESD Floor
[11 min read, 7 min video]
Post Summary
This how-to article explains several ways to properly ground an ESD floor. Detailed instructions are supported by illustrations for an easy-to-follow field guide.
Grounding an ESD floor is straightforward and easy.
Conductive adhesive eliminates the need for expensive copper equipotential grounding grids of the past.
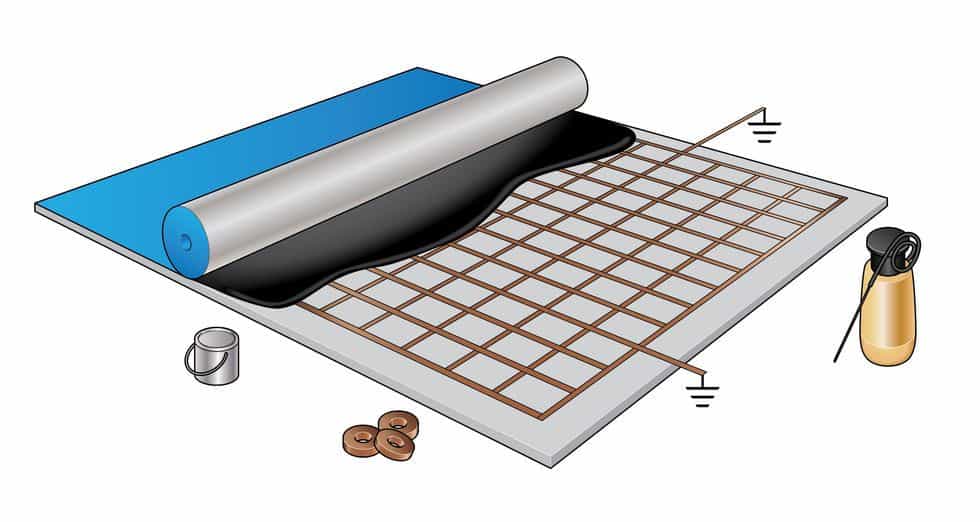





Grounding Method 1: Easiest
Grounding to an ESD Electrical Outlet
Grounding conductive and static-dissipative tile and sheet flooring to an AC electrical outlet is the easiest and most common grounding method.
Caution: Only use electrical receptacles/outlets that have been previously tested using an approved circuit tester complying with CSA and/or UL standards.
Required materials:
- Screwdriver
- 24-inch copper grounding strap
- ESD flooring
- Conductive adhesive.
One copper grounding strap should be installed for every 1000 square feet of ESD flooring. Each room should have at least one grounding strap.
Step 1

Remove center screw on cover of AC electrical outlet using a screwdriver.
Step 2

Locate and remove grounding screw inside AC electrical outlet.
Step 3
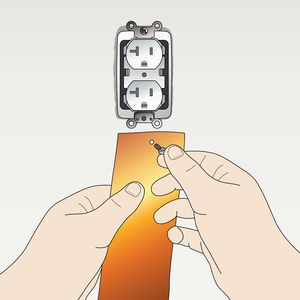
Punch small hole in 24″ copper grounding strap (provided with StaticWorx ESD flooring). The hole should be smaller than the head of the screw removed in Step 2.
Step 4
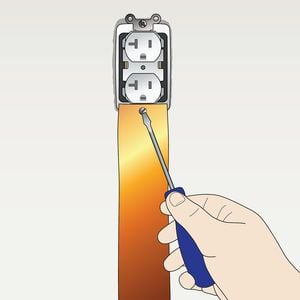
Secure copper strap to the AC electrical outlet with the same screw removed in step 2.
Step 5
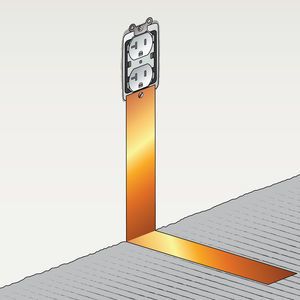
Fold copper at a 90-degree angle at the point where the wall meets the floor. Lay remainder of copper strap flat on the subfloor. The strap can be placed directly on the concrete subfloor in advance of installation or pressed into the conductive adhesive during installation.
At least 6 inches of copper should contact the floor. If the copper is applied directly to bare concrete or another subfloor, it will need to be covered with conductive adhesive during the installation.
Step 6
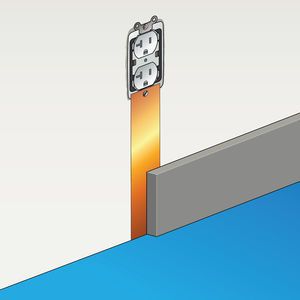
Cover copper strap on floor with conductive adhesive and new flooring material. For a cleaner installation, copper should be covered by wall base.
Step 7

Finish installation by re-attaching AC outlet cover with screw removed in step 1.
One copper grounding strap should be installed for every 1000 square feet of ESD flooring. Each room should have at least one grounding strap.
Step 1

Remove center screw on cover of AC electrical outlet using a screw driver.
Step 2

Locate and remove grounding screw inside AC electrical outlet.
Step 3

Punch small hole in 24″ copper grounding strap (provided with StaticWorx ESD flooring). The hole should be smaller than the head of the screw removed in Step 2.
Step 4

Secure copper strap to the AC electrical outlet with the same screw removed in step 2.
Step 5
Allow 24″ copper strap to run down wall to subfloor (concrete, etc.).
Fold copper at a 90-degree angle at the point where the wall meets the floor. Lay remainder of copper strap flat on the subfloor. The strap can be placed directly on the concrete subfloor in advance of installation or pressed into the conductive adhesive during installation.
At least 6 inches of copper should contact the floor. If the copper is applied directly to bare concrete or another subfloor, it will need to be covered with conductive adhesive during the installation.
Step 6

Cover copper strap on floor with conductive adhesive and new flooring material. For a cleaner installation, copper should be covered by wall base.
Step 7

Finish installation by re-attaching AC outlet cover with screw removed in step 1.

A Ground Plug Adapter is equipped with three indicating lights. The ONLY indication that is acceptable for the Ground Plug Adapter to be in use is with the two outer “CIRCUIT OK” lights energized, i.e., Lights #1 and #3 ON, Light #2 OFF.
*———-CIRCUIT OK———*
| Light #1 | Light #2 | Light #3 |
| Yellow | Red | Clear |
If any other condition exists, do not use the receptacle or the Ground Plug Adapter until tested and approved by a qualified electrician.
Examples of wiring defects include, but are not limited to the conditions described below:
- OPEN GROUND WIRE – The equipment grounding conductor is not complete.
- REVERSE POLARITY – The hot and the neutral circuit conductors are reversed.
- OPEN HOT WIRE – The hot circuit conductor is open from a blown fuse, tripped circuit breaker, switch off, broken wire, etc.
- OPEN NEUTRAL WIRE – The neutral circuit conductor is open.
- HOT AND GROUND REVERSED – The hot circuit conductor and the grounding conductor are reversed.
- HOT ON NEUTRAL AND HOT OPEN – The hot circuit conductor is connected to neutral terminal and the hot terminal is unwired.
✓ visual selector guide;
✓ walking body voltage/low static generation;
✓ resistance requirements and testing;
✓ ESD flooring comparison;
✓ industry standards & test methods;
✓ key ESD terms
Alternative Grounding Methods
Grounding Method 2: Grounding to a Natural Earth Ground
If the floor will be installed on-grade or below grade, a copper grounding rod can be driven into the ground, creating an earth ground for the floor.
Step 1
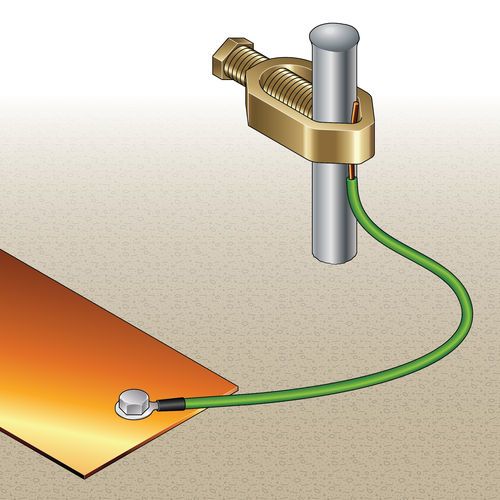
Step 2
Attach the copper-grounding strap to the exposed end of the rod using a grounding clamp, usually sourced from the same manufacturer as the grounding rod (refer to www.stormgrounding.com.) If necessary, a #10 or #12 wire can be attached to the grounding rod.
Step 3
Run the wire from the rod to the grounding strap, and tie it to the strap with a wire nut.
If the floor will be installed on-grade or below grade, a copper grounding rod can be driven into the ground, creating an earth ground for the floor.
Step 1
Drive the 4- to 6-foot rod into the ground until only 2 or 3 inches of the rod remains exposed.
Step 2
Attach the copper-grounding strap to the exposed end of the rod using a grounding clamp, usually sourced from the same manufacturer as the grounding rod (refer to www.stormgrounding.com.) If necessary, a #10 or #12 wire can be attached to the grounding rod.
Step 3
Run the wire from the rod to the grounding strap, and tie it to the strap with a wire nut.
Grounding Method 3: Grounding to an Earth Ground
If the building is constructed with exposed steel support columns, the copper grounding strap can be attached directly to one or more of the columns.
Step 1
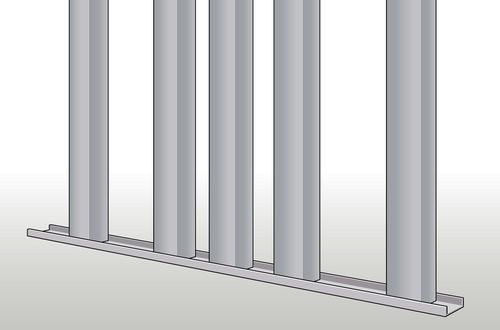
Step 2
Drill a hole in the support column.
Step 3
With a grounding screw or clamp, attach the end of the copper strap directly to the column. Or mount a grounding clamp to the column and use it to clamp the copper strap.
Copper grounding straps should be attached to aluminum studs using sheet metal screws and a washer.

Step 4
A continuity test should be conducted with a volt ohm meter (VOM) to confirm a compliant electrical ground connection between the copper strap and electrical ground.
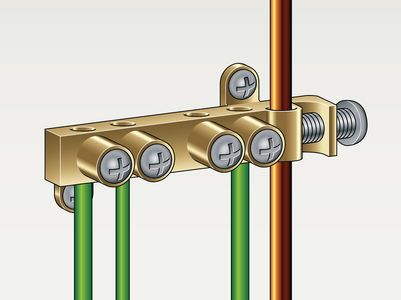
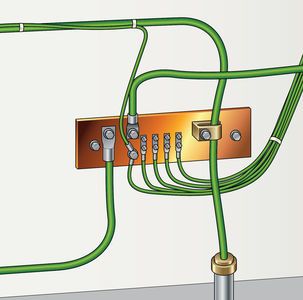
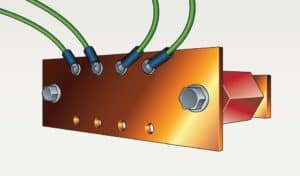
Copper bus bars can serve as a dedicated Common Point ESD Flooring Ground Connection.
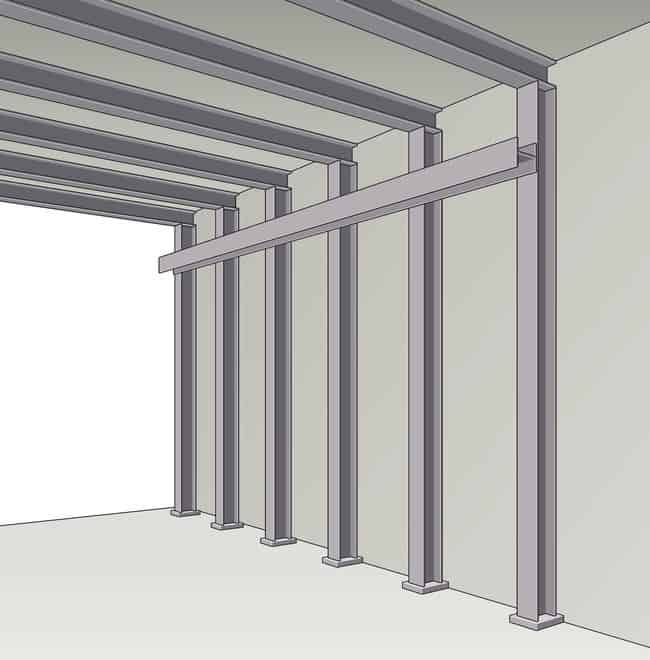
Copper ground straps may also be adhered to structural I beams.
Note: The beams must be bare metal. Paints and coatings must be removed from beams prior to attaching copper straps.
If the building is constructed with exposed steel support columns, the copper grounding strap can be attached directly to one or more of the columns.
Step 1
Affix the grounding strap to the tile as described in paragraph one.
Step 2
Drill a hole in the support column.
Step 3
With a grounding screw or clamp, attach the end of the copper strap directly to the column. Or mount a grounding clamp to the column and use it to clamp the copper strap.
Copper grounding straps should be attached to aluminum studs using sheet metal screws and a washer.
Step 4
A continuity test should be conducted with a volt ohm meter (VOM) to confirm a compliant electrical ground connection between the copper strap and electrical ground.
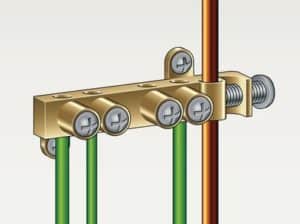
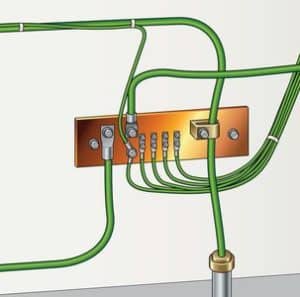
Copper bus bars can serve as a dedicated Common Point ESD Flooring Ground Connection.
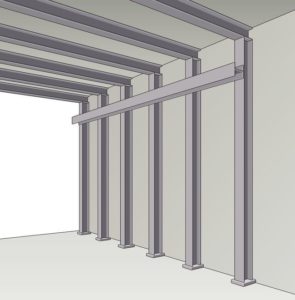
Copper ground straps may also be adhered to structural I beams.
Note: The beams must be bare metal. Paints and coatings must be removed from beams prior to attaching copper straps.
Helpful Definitions
AC Equipment Ground
a) The ground point at which the equipment grounding conductor is bonded to any piece of equipment, at the equipment end of the conductor in a single-phase 120VAC electrical service.
b) The 3rd wire (green/green with yellow strap) terminal of a receptacle.
c) The entire low impedance path (electrically equivalent to the equipment grounding conductor) from a piece of electrical equipment to the neutral bus at the main service equipment.
Common Connection Point
A device or location (less than 1 ohm within itself) where the conductors of two or more ESD technical elements are connected in order to bring the ungrounded ESD technical elements to the same electrical potential through equipotential bonding.
Common Point Ground
A grounded device or location where the conductors of one or more technical elements are bonded.
a) A conducting connection, whether intentional or accidental between an electrical circuit or equipment and the earth, or to some conducting body that serves in place of the earth.
b) The position or portion of an electrical current at zero potential with respect to the earth.
c) A conducting body, such as the earth or the hull of a steel ship used as a return path for electric currents and as an arbitrary zero reference point.
ESDA Technical Requirements – Grounding
| Equipment Grounding Conductor | ANSI/ESD S6.1 | < 1.0 ohm impedance |
| Auxiliary Ground | ANSI/ESD S6.1 | < 25 ohms to the Equipment Grounding Conductor |
| Equipotential Bonding | ANSI/ESD S6.1 | < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms(3) |
Please note: StaticWorx carpet, tile, and sheet flooring installations utilize conductive adhesives. Copper ground straps are supplied with every StaticWorx flooring shipment.
Get in Touch
The form below will help us better understand your needs and get you as quickly as possible to the right person. We look forward to helping you solve your static problem!
You can expect a response within 24 hours. For faster service, please give us a call: 617-923-2000
"*" indicates required fields
Visit our privacy policy to find out how we process data.
Learning Center Articles
- ESD Basics
- Installation & Maintenance
- Selecting & Specifying an ESD Floor
- Technical Information
- 7 Common Mistakes Selecting an ESD floor
- A Guide to ESD Flooring Selection
- Avoid Costly Failures: What You Need to Know When Specifying ESD Flooring
- Choosing ESD Flooring for:
- ESD Footwear: What Is It and When Is It Necessary?
- ESD Footwear for Electronics Manufacturing and Handling Applications
- Facility Managers’ Guide to Selecting ESD Flooring
- The Need for Due Diligence in Specifying Static-Free Flooring
- Standard of Care for Specifying Floors in Mission-Critical Spaces
- Understanding the Hidden Costs of ESD Flooring

StaticWorx high-performance static-control floors protect electronic components, explosives, and high-speed computers from damage caused by static electricity. ESD flooring is part of a system. Choices should always be based on objective, researched evidence. When you partner with us, we look at all possible items that may need to integrate with the floor, and, focusing on your goals and objectives, help you find the right floor for your application.











