GLOSSARY: Static-dissipative Flooring
Static-dissipative floors are defined by a property called electrical resistance. Electrical resistance, measured in ohms, is a material’s ability to resist, or stop, the flow of electricity.
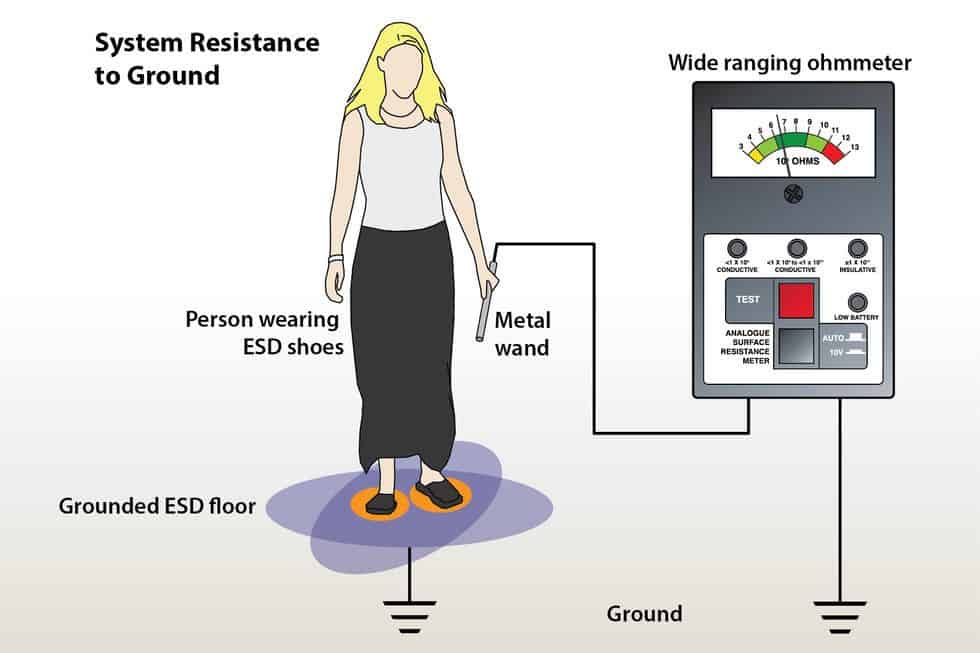
One of the two important parameters for describing a static control floor is resistance to ground or path to ground. In order to qualify as static dissipative, a floor must have an electrical resistance to ground that’s > 1.0 x 10E6 (one million ohms) AND ≤ 1 x 10E9 (one billion ohms).
The term “static dissipative” should not be confused with the terms “conductive,” “antistatic” or “low charge generating.”
A static-control floor can be dissipative (or conductive) and still generate charges significant enough to cause an ESD event.
Note: the secondary definition below does NOT apply to ESD flooring or flooring materials.
2) Another definition of static dissipative is: a material that can conduct an electrical charge and has an inherent resistivity range between 1 x 10E4 ohms and 1 x 10E11 ohms. Sometimes referred to as electrically dissipative.
Learning Center Articles
- ESD Basics
- Installation & Maintenance
- Selecting & Specifying an ESD Floor
- Technical Information
- 7 Common Mistakes Selecting an ESD floor
- A Guide to ESD Flooring Selection
- Avoid Costly Failures: What You Need to Know When Specifying ESD Flooring
- Choosing ESD Flooring for:
- ESD Footwear: What Is It and When Is It Necessary?
- ESD Footwear for Electronics Manufacturing and Handling Applications
- Facility Managers’ Guide to Selecting ESD Flooring
- The Need for Due Diligence in Specifying Static-Free Flooring
- Standard of Care for Specifying Floors in Mission-Critical Spaces
- Understanding the Hidden Costs of ESD Flooring

StaticWorx high-performance static-control floors protect electronic components, explosives, and high-speed computers from damage caused by static electricity. ESD flooring is part of a system. Choices should always be based on objective, researched evidence. When you partner with us, we look at all possible items that may need to integrate with the floor, and, focusing on your goals and objectives, help you find the right floor for your application.








